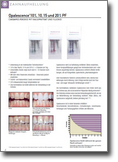
Types of stunning
Many people are afraid of pain at the dentist. But thanks to the many different types of anesthesia, you no longer need to be afraid of pain. Thanks to the different types of anesthesia, nothing stands in the way of a relaxed and painless treatment.
Different types of anesthesia:
Surface anesthesia
Surface anesthesia – for example with a spray – serves to anesthetize the mucous membrane on the surface in order to reduce the puncture pain of the subsequent injection, especially in children.
Cold anaesthesia
Cold anesthesia is a form of local anesthesia in which the affected areas are made insensitive to pain by cold, e.g. with ice sprays. Ordinary water ice (ice packs), which melt at a temperature of 0 °C, can significantly reduce the sensation of pain. The risk of tissue damage is significantly lower with ice packs than with cold sprays.
Infiltration anesthesia
Infiltration anesthesia is designed to eliminate the pain in the vicinity of the injection site. The anesthetic solution penetrates the bone and numbs the teeth. However, this only works in the upper jaw and anterior region of the lower jaw.
Line anesthesia
If the posterior region of the lower jaw or a larger area is to be anesthetized, conduction anesthesia is used. Here, the anesthetic is injected near the nerve that supplies the corresponding jaw area. With the beginning of the effect, the lower lip and often also the half of the tongue becomes numb.
Infraorbital anesthesia
Infiltration anaesthesia is considered a standard anaesthetic procedure, especially in the upper jaw area, and is a variant of local anesthesia in which the anesthetic is injected directly into the tissue in the surgical area. To where the nerves that are responsible for the pain sensation run. Normally, the affected tooth and the two adjacent teeth are anesthetized during dental treatment. The local anesthetic is inserted by the dentist around the root tip of the tooth to be treated directly under the mucous membrane. The aim is to distribute the solution between the tissue gaps and the periosteum as well as to reach the jawbone and the proximity of the nerve fibers. There, infiltration anaesthesia causes a blockage of the sensitive nerve tracts.
Medibularanesthesia
Mandibular anesthesia is the anesthesia of the mandibular nerve at the nerve entry site into the lower jaw. In the case of the posterior molars, anesthesia directly at the root of the tooth is no longer possible due to the thick bone cortex of the lower jaw. Therefore, the mandibular nerve is switched off at the dentist directly at its entry point into the lower jaw, which then has the consequence that almost all teeth of one lower jaw half and half of the lip are anesthetized.
Analog sedation
With this form of anesthesia, the patient retains consciousness, but still does not feel pain. Analog sedation eliminates the pain with the help of an injection into the arm. The patient reacts to physical stimuli and the address of the practitioner, although he is in a sleep-like state. Since analogue sedation does not prevent the pain, but only influences the sensation, an additional local anesthesia, the so-called local anesthesia, usually remains unavoidable.
Intraligamentary anaesthesia
In intraligamentary anaesthesia, a very thin needle and a special syringe are injected directly between the tooth and its bone compartment. This may be necessary if complete freedom from pain cannot be achieved with other types of anesthesia.
After treatment with anesthesia:
The responsiveness can be significantly reduced by any type of anesthesia. Therefore, you should not drive vehicles after anesthesia and be careful in traffic. It is best to have an accompanying person bring you home. Also avoid the consumption of alcohol and take additional painkillers only at home. Only when the numbness has completely disappeared should you eat and drink, otherwise you could bite on the anesthetized areas.
If your toddler has been anesthetic, watch closely as the effects subside. If children chew on the anesthetized area, it can lead to serious injuries to the lip, cheeks and tongue because of the numbness.
further information on the subject of types of anaesthesia
 |
|||||